When building scalable applications, job queues are essential. They help manage workload, handle traffic spikes, and ensure system reliability. But what happens when your queue system itself becomes a source of complexity?
At OpenPanel, we process millions of analytics events daily. Each event needs to be queued, processed, and stored efficiently. We started with BullMQ, which served us well initially. However, as our traffic grew, we encountered a challenge that many high-throughput systems face: race conditions when processing related events.
The Concurrency Problem
Imagine you're tracking user behavior on a website. A single user might trigger multiple events within milliseconds: a page view, a click, and a form submission. These events arrive at your queue almost simultaneously, and if processed in parallel by different workers, they can create race conditions.
Traditional solutions involve complex locking mechanisms, distributed locks, or careful transaction management. While these work, they add complexity and can become bottlenecks themselves. We needed something better.
The ideal solution was clear: process events from the same user sequentially while maintaining overall system throughput. This would eliminate race conditions at the architectural level rather than trying to handle them in application code.
Why Not BullMQ Pro?
BullMQ actually offers this exact feature through their "Group" functionality, but it's only available in their Pro version. For a commercial SaaS product, paying for BullMQ Pro makes perfect sense. However, OpenPanel is open source and self-hostable.
Requiring our users to purchase a commercial license for a critical dependency would contradict our core mission. We believe in providing a complete, truly open-source analytics solution that anyone can run without hidden costs or proprietary dependencies.
This philosophy drove us to create GroupMQ: an open-source queue system that makes job grouping a first-class feature, not a premium add-on.
Introducing GroupMQ
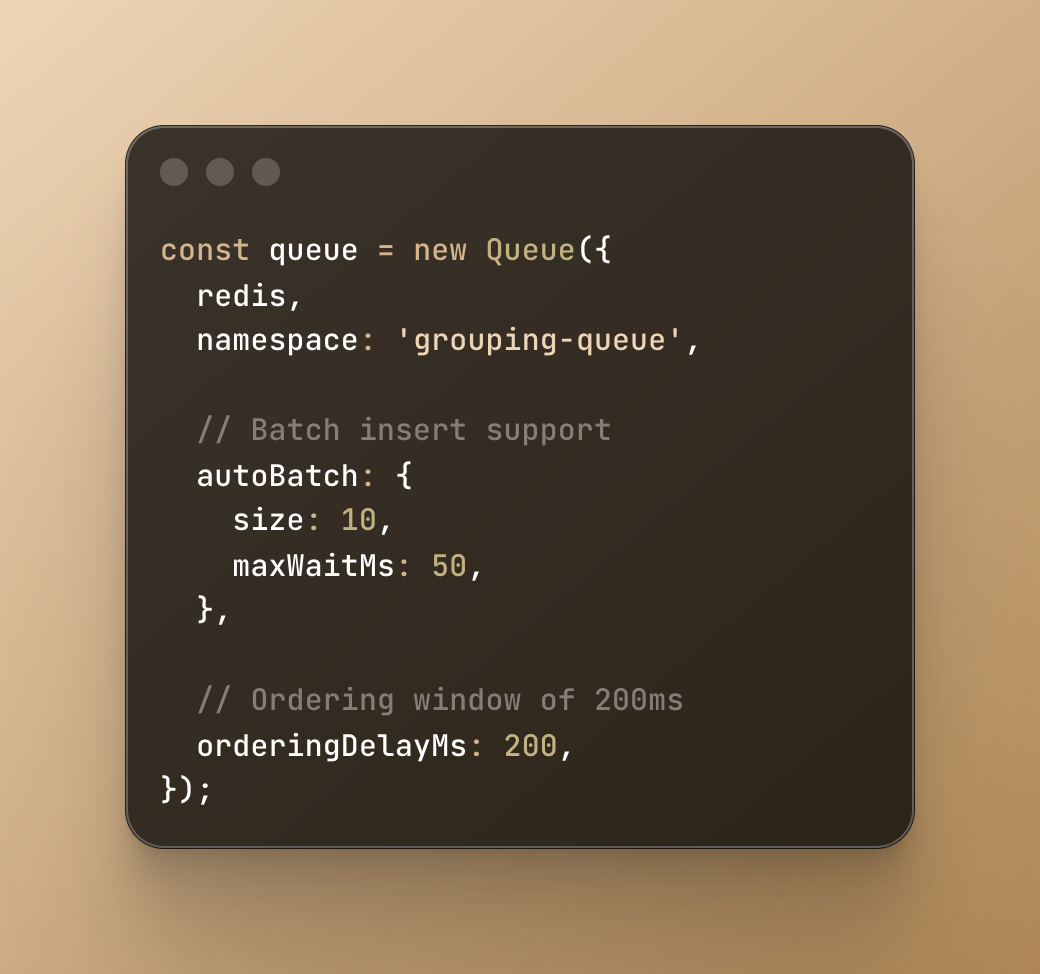
GroupMQ is a Redis-based queue system inspired by BullMQ but designed from the ground up with job grouping as its core feature. It ensures that jobs within the same group are processed sequentially while different groups run in parallel.
Here's what makes GroupMQ special:
Intelligent Group Processing: Jobs are automatically organized by group IDs. The system guarantees that only one job per group is processed at any given time, completely eliminating race conditions for related operations.
Fair Scheduling: Unlike naive implementations that might let one busy group block others, GroupMQ uses a round-robin approach to ensure all groups get processing time. This prevents any single group from monopolizing worker resources.
Familiar API: If you've used BullMQ, you'll feel right at home. We've maintained similar patterns and conventions, making migration straightforward. The main difference is that group assignment is mandatory and built into every operation.
Redis-Native Performance: Built directly on Redis data structures, GroupMQ leverages Redis's atomic operations for maximum performance and reliability. There's no additional overhead compared to other Redis-based queues.
Real-World Use Cases
GroupMQ shines in scenarios where you need to maintain order within related operations:
Analytics Processing: Process events from the same user sequentially to maintain accurate session tracking and prevent duplicate counting.
E-commerce Orders: Handle order updates, payment processing, and inventory changes for the same order ID without race conditions.
Notification Systems: Ensure notifications for the same recipient are processed in order, preventing confusing out-of-sequence messages.
Multi-tenant Applications: Process jobs for each tenant in isolation while maintaining overall system throughput.
Import/Export Operations: Handle file processing where multiple operations on the same resource must happen sequentially.
BullBoard Compatibility
One of BullMQ's strengths is its ecosystem, particularly BullBoard for queue monitoring. We've ensured that GroupMQ maintains compatibility with BullBoard through an adapter.
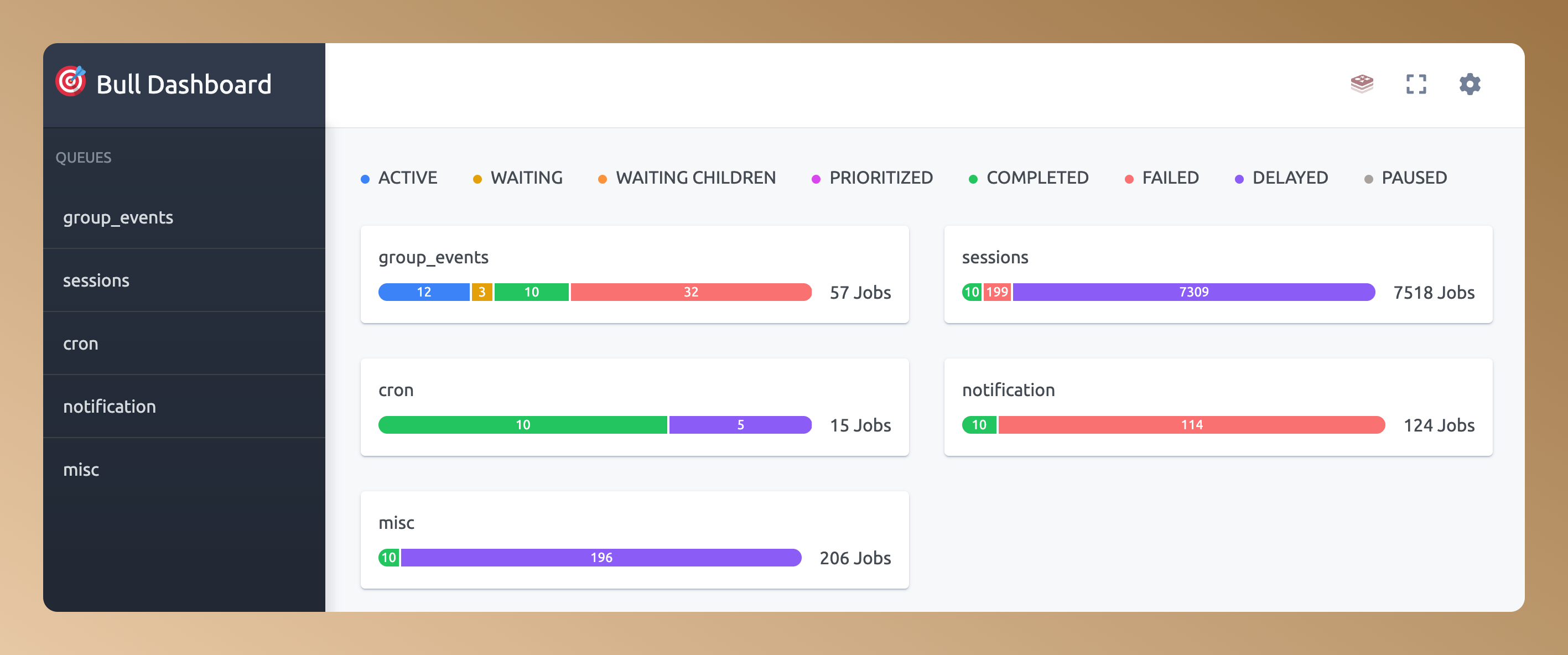
This means you can continue using your existing monitoring setup. View job counts, processing rates, and failed jobs just as you would with BullMQ. The only difference is that jobs are now organized by groups, giving you better visibility into your grouped processing patterns.
Migration from BullMQ
Migrating from BullMQ to GroupMQ is designed to be as smooth as possible. The main changes involve:
-
Adding Group IDs: Every job must have a group ID. This is typically derived from your existing data (user ID, order ID, etc.)
-
Updating Job Addition: Update
queue.add()to includegroupIdin the options object -
Worker Updates: Workers now receive job objects with both
dataandgroupIdproperties
Here's a quick example of the differences:
// BullMQ
import { Queue, Worker } from 'bullmq';
import IORedis from 'ioredis';
const connection = new IORedis({ maxRetriesPerRequest: null });
const queue = new Queue('events');
await queue.add('process-event', { userId: 123, action: 'click' });
const worker = new Worker(
'events',
async (job) => {
console.log(job.data); // { userId: 123, action: 'click' }
},
{ connection }
);
// GroupMQ
import Redis from 'ioredis';
import { Queue, Worker } from 'groupmq';
const redis = new Redis();
const queue = new Queue({ redis, namespace: 'events' });
await queue.add({
groupId: 'user-123',
data: { userId: 123, action: 'click' }
});
const worker = new Worker({
queue,
handler: async (job) => {
console.log(job.data); // { userId: 123, action: 'click' }
console.log(job.groupId); // 'user-123'
},
});
worker.run();The main differences are:
- Queue constructor: BullMQ takes a queue name string, GroupMQ takes an options object with
redisandnamespace - Adding jobs: BullMQ takes job name and data as separate parameters, GroupMQ takes a single object with
groupIdanddata - Workers: BullMQ takes queue name, handler function, and options. GroupMQ takes an options object with
queueandhandler, then requires callingrun() - Job object: GroupMQ jobs include both
job.dataandjob.groupIdproperties
Performance Characteristics
GroupMQ's performance profile differs from traditional queues in interesting ways:
Sequential Within Groups: Jobs in the same group process one at a time. This might seem like a limitation, but it's exactly what prevents race conditions. The throughput for a single group matches single-threaded processing speed.
Parallel Across Groups: Different groups process completely in parallel. With enough groups, you can saturate all available workers just like a traditional queue system.
Predictable Latency: Since groups process independently, a slow job in one group doesn't impact others. This isolation provides more predictable performance characteristics.
Memory Efficiency: Group organization in Redis is optimized to minimize memory usage while maintaining fast access patterns.
Advanced Features
Beyond basic job grouping, GroupMQ includes several advanced features:
Delayed Jobs: Schedule jobs to run after a specific delay, useful for scheduled tasks or retry backoffs.
Repeating Jobs: Configure cron-like patterns to create recurring jobs on a schedule.
Job Retries: Built-in retry mechanism with configurable attempts and backoff strategies. Failed jobs can be automatically retried or moved to dead letter storage.
Ordering Strategies: Choose between different ordering methods ('none', 'scheduler', or 'in-memory') to handle out-of-order job arrivals based on your use case.
Graceful Shutdown: Workers can complete processing current jobs before shutting down, ensuring data consistency.
BullBoard Integration: Monitor your queues using the familiar BullBoard interface through the provided adapter.
When to Choose GroupMQ
GroupMQ is the right choice when:
- You need to process related jobs sequentially
- Race conditions are a concern in your system
- You want to eliminate complex locking logic
- Your workload naturally groups into independent streams
- You're building an open-source project and need a fully open queue solution
It might not be the best fit if:
- Your jobs are completely independent
- You need every job to process as fast as possible regardless of relationships
- You have very few natural groupings in your data
- You're already using BullMQ Pro and happy with it
Getting Started
Installing GroupMQ is straightforward:
npm install groupmqBasic usage follows familiar patterns:
import Redis from 'ioredis';
import { Queue, Worker } from 'groupmq';
const redis = new Redis();
const queue = new Queue({
redis,
namespace: 'events',
});
// Add a job to a group
await queue.add({
groupId: 'user-123',
data: { userId: 123, action: 'pageview' }
});
// Process jobs with a worker
const worker = new Worker({
queue,
handler: async (job) => {
console.log(`Processing ${job.data.action} for ${job.groupId}`);
// Your processing logic here
},
});
worker.run();Open Source Philosophy
GroupMQ embodies our commitment to true open-source software. It's MIT licensed, accepts community contributions, and will never have a "pro" version with essential features locked away.
We built GroupMQ because we needed it for OpenPanel, but we're releasing it as a standalone project because we believe others face similar challenges. The best solutions emerge when real-world problems meet open collaboration.